Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM8SXYG)
| Drug Name |
Lamotrigine
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Crisomet; Labileno; Lamictal; Lamictin; Lamiktal; Lamitor; Lamotrigina; Lamotriginum; Desitin Brand of Lamotrigine; Faes Brand of Lamotrigine; Glaxo Wellcome Brand of Lamotrigine; GlaxoSmithKline Brand of Lamotrigine; Juste Brand of Lamotrigine; Lamictal Cd; Lamictal ODT; Lamictal XR; Lamotrigina [Spanish]; Lamotriginum [Latin]; BW 430C; GI 267119X; GW 273293; L 3791; BW-430C; EUR-1048; Lamictal (TN); Lamictin (TN); Lamotrigine [USAN:INN:BAN]; Lamotrigine (JAN/USAN/INN); 3,5-Diamino-6-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazine; 3,5-Diamino-6-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-as-triazine; 3,5-diamino-6-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-as-triazine; 6-(2,3-Dichlorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazine-3,5-diamine; 6-(2,3-Dichlorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazine-3,5-diyldiamine; 6-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazine-3,5-diamine
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Anticonvulsants
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
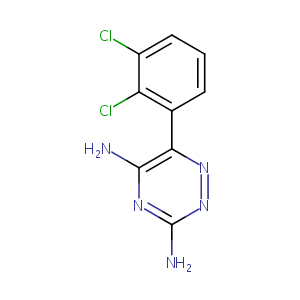 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 256.089 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 1.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Lamotrigine (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2622). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 3 | Critical Evaluation of Human Oral Bioavailability for Pharmaceutical Drugs by Using Various Cheminformatics Approaches | ||||
| 4 | Lamictal FDA Label | ||||
| 5 | Gomes RL, Meredith W, Snape CE, Sephton MA: Analysis of conjugated steroid androgens: deconjugation, derivatisation and associated issues. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2009 Jul 12;49(5):1133-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2009.01.027. Epub 2009 Jan 31. | ||||
| 6 | Lamotrigine clinical pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1993 Dec;25(6):433-43. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199325060-00003. | ||||
| 7 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 8 | The effects of lamotrigine on the acquisition and expression of morphine-induced place preference in mice. Pak J Biol Sci. 2009 Jan 1;12(1):33-9. | ||||
| 9 | Lamotrigine is a substrate for OCT1 in brain endothelial cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 Mar 15;83(6):805-14. | ||||
| 10 | Several major antiepileptic drugs are substrates for human P-glycoprotein. Neuropharmacology. 2008 Dec;55(8):1364-75. | ||||
| 11 | Drug-drug interactions for UDP-glucuronosyltransferase substrates: a pharmacokinetic explanation for typically observed low exposure (AUCi/AUC) ratios. Drug Metab Dispos. 2004 Nov;32(11):1201-8. | ||||
| 12 | Variation in glucuronidation of lamotrigine in human liver microsomes. Xenobiotica. 2009 May;39(5):355-63. | ||||
| 13 | Studies on induction of lamotrigine metabolism in transgenic UGT1 mice. Xenobiotica. 2009 Nov;39(11):826-35. | ||||
| 14 | Effects of anticonvulsants on human p450c17 (17alpha-hydroxylase/17,20 lyase) and 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2. Epilepsia. 2005 Mar;46(3):444-8. | ||||
| 15 | Genetic association study of treatment response with olanzapine/fluoxetine combination or lamotrigine in bipolar I depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 2010 May;71(5):599-605. doi: 10.4088/JCP.08m04632gre. Epub 2009 Dec 15. | ||||
| 16 | Inhibition of human aromatase complex (CYP19) by antiepileptic drugs. Toxicol In Vitro. 2008 Feb;22(1):146-53. | ||||
| 17 | Functional evaluation of polymorphisms in the human ABCB1 gene and the impact on clinical responses of antiepileptic drugs. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2008 May;18(5):390-402. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0b013e3282f85e36. | ||||
| 18 | Bioactivation of lamotrigine in vivo in rat and in vitro in human liver microsomes, hepatocytes, and epidermal keratinocytes: characterization of thioether conjugates by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry and high field nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Chem Res Toxicol. 2010 Jan;23(1):159-70. doi: 10.1021/tx9003243. | ||||
| 19 | Belcastro V, Costa C, Striano P "Levetiracetam-associated hyponatremia." Seizure 17 (2008): 389-90. [PMID: 18584781] | ||||
| 20 | Warrington SJ, Ankier SI, Turner P "Evaluation of possible interactions between ethanol and trazodone or amitriptyline." Neuropsychobiology 15 (1986): 31-7. [PMID: 3725002] | ||||
| 21 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 22 | American Epilepsy Society "FDA Safety Warning on the Cardiac Effects of Lamotrigine: An Advisory from the Ad Hoc ILAE/AES Task Force. [PMID: 33641454] | ||||
| 23 | Ebert U, Thong NQ, Oertel R, Kirch W "Effects of rifampicin and cimetidine on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of lamotrigine in healthy subjects." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 56 (2000): 299-304. [PMID: 10954343] | ||||
| 24 | Blakely KM, Drucker AM, Rosen CF "Drug-induced photosensitivity-an update: Culprit drugs, prevention and management." Drug Saf 42 (2019): 827-47. [PMID: 30888626] | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Zulresso (brexanolone). Sage Therapeutics, Inc., Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 26 | Product Information. Reyvow (lasmiditan). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Addyi (flibanserin). Sprout Pharmaceuticals, Raleigh, NC. | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. Thalomid (thalidomide). Celgene Corporation, Warren, NJ. | ||||
| 29 | Bigham S, McGuigan C, MacDonald BK "Reduced absorption of lipophilic anti-epileptic medications when used concomitantly with the anti-obesity drug orlistat." Epilepsia 47 (2006): 2207. [PMID: 17201727] | ||||
| 30 | Product Information. Alphagan (brimonidine ophthalmic). Allergan Inc, Irvine, CA. | ||||
| 31 | Hansen BS, Dam M, Brandt J, et al "Influence of dextropropoxyphene on steady state serum levels and protein binding of three anti-epileptic drugs in man." Acta Neurol Scand 61 (1980): 357-67. [PMID: 6998251] | ||||
| 32 | Sekar M, Mimpriss TJ "Buprenorphine, benzodiazepines and prolonged respiratory depression." Anaesthesia 42 (1987): 567-8. [PMID: 3592200] | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Zanaflex (tizanidine). Acorda Therapeutics, Hawthorne, NY. | ||||
